How Corporate KYC is important? The Challenges Faced and Documents Required
How Corporate KYC is important? The Challenges Faced and Documents Required
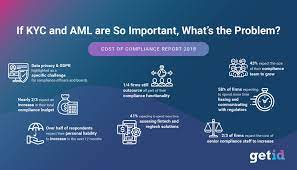
Corporate KYC (know your customer) protocols help financial organisations identify and understand their clients. Before beginning any type of collaboration with a financial institution, the user must complete KYC following normal operating norms.
This article seeks to inform you of the significance of corporate KYC and the necessary paperwork.
Corporate KYC: A Quick Summary:
Before letting a company or corporation and its owners create an account at a financial institution. Corporate KYC verifies their validity. By doing this, it may be possible to find shelf businesses, offshore accounts, and shell companies that legitimise illegal funds. Investigations into false positives are expensive for regulated firms even if they are frequently unneeded. If businesses don’t conduct thorough PEP (politically exposed person) and sanctions screening. The regulator may impose severe fines (even if a false positive). The following are the three crucial puzzle pieces:
- Identification of the client
- Customer Due Diligence
- Customer tracking
The Importance of Corporate KYC
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) get into being by the G7 in 1989. When Pablo Escobar’s cocaine empire broke into the world banking system. After 9/11, it added Anti-Terrorist Funding (ATF) to its list of priorities. By formulating standards and promoting the effective application of legislative, administrative, and tactical measures to combat money laundering, terrorism funding, and related concerns, the FATF seeks to safeguard the global financial system against illegal behaviour. India responded by enacting the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) in 2002 to stop the financing of terrorism.
The absence of regulations governing KYC caused severe occurrences that were crucial in completely changing the global order. Corporate KYC is vital since it enables a business to confirm the legitimacy of its client, another business. Establishing the steps to do in the event that risk connects to the customer is part of the onboarding process.
Required Documents for Corporate KYC
The procedure used for a KYC depends on the kind of regulatory agency in question; there is no universal approach. The central bank only issues directives, which regulatory bodies may interpret as broadly but not precisely as intended, depending on their level of risk tolerance. However, the following are some of the surface-level KYC requirements for corporates:
- a copy of the CIN mentioned in the certificate of the establishment (corporate identity number)
- a copy of the articles of incorporation and memorandum (AOA).
- PAN (permanent account number) card copy for the business.
- a board of directors resolution authorising the opening of a bank account and the selection of its authorised users.
- Pictures and signature cards with firm attestations must use to identify authorised signatories.
- Copies of identification and address evidence together with the permanent account number (PAN) of the managers, officers, or staff members with the authority to do business on the company’s behalf.
- Director identification number (DIN), list of directors, and a replica of Form 32 (if directors differ from AOA)
- A true copy of the business registration certificate (public limited company).
- Apart from the aforementioned information, a copy of evidence must also include the company’s name, major location of the business, postal address, and phone or fax number. (Telephone bill that is no more than two months old.)
Corporate KYC Process Automation
Corporate KYC processes can automate to achieve a number of advantages, including lower costs, more efficiency, decreased risk, and improved client satisfaction.
There are numerous strategies one can use to automate the KYC procedures. AI algorithms use with third-party API connections, intelligent document processing (IDP), robotic process automation (RPA), and IDP.
The aforementioned technologies are used to speed up the screening, identification, and verification of people while also automating workflow operations and gathering data from documents. Staff employees can swiftly review and assess supplied papers by confirming client identity.
Organizational KYC: The Problems
The KYC processes used by corporations are more rigorous, complex, and expensive than those used by individuals. The following are some of the main issues with the corporate KYC process:
Faulty Data:
When attempting to confirm a corporate customer’s KYC information, any financial institution will run into errors and inconsistencies in corporate registration documents and filing histories, especially in another jurisdiction. Inaccurate data can be dangerous since financial organisations rely on their decisions being based on data.
False Negatives:
Investigations into false positives are expensive for regulated organisations even though they are frequently unneeded. If companies don’t conduct thorough PEP and sanctions screening, they run the danger of receiving severe fines from the regulator (even if a false positive).
Onboarding is time-consuming and generally manual:
Financial institutions and businesses that are implementing corporate KYC are persistently concerned about the actual cost and resources required to vet prospective clients before onboarding. The onboarding institution and potential client may give up due to the time and effort required, or the business client may decide not to onboard.
Ongoing Monitoring
problems with corporate KYC persist even after consumer onboarding. Ownership, corporate interests, and organisational structures may alter. Therefore, even if a KYC check was successful at onboarding, a business can later cease to be compliant. Due to the dynamic nature of AML/ATF laws around the world, banking, financial services, and insurance (BFSIs) may need to reclassify current customers who were previously considered low-risk.
Summing it up:
To ensure the existence of a system of checks and balances to uncover actions like financial fraud, money laundering, and terrorist funding. Corporate KYC is a crucial process. Due to the complexity of the corporate KYC process, it is common for businesses to get overburdened with paperwork. Before completing even one corporate KYC.
But owing to technology, this is quickly changing. Machine learning, IDP, and RPA use to automate the corporate KYC process. The market for KYC services for corporate clients is expanding rapidly and was previously unexplored.



